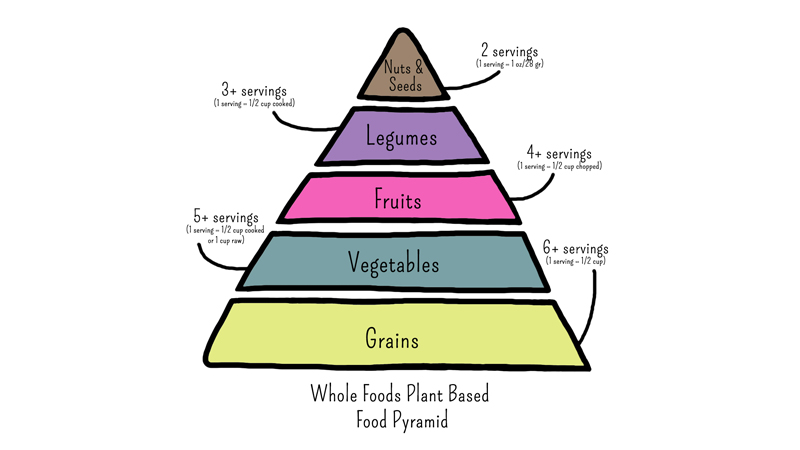
Becoming vegan doesn’t necessarily mean you will automatically have a healthier life. In general, if you switch to a plant-based diet, your intake of fat and cholesterol is dramatically reduced, but if you stuff yourself with vegan cheese, margarine, and fried snacks, chances are, you won't be getting much healthier. If you want to care for the animals, ánd your body, switching to a Whole Food Plant Based diet (WFPB) might be something to consider.
What is a Whole Food Plant Based (WFPB) diet?
A WFPB diet consists wholly of plants and does not contain any animal ingredients and emphasizes the use of fresh, whole food ingredients and a minimum of processed foods, added sodium, sugar, and fat. It is a diet of (starchy) vegetables, fruit, whole grains, and legumes supplemented with nuts and seeds1.
What it is not
A WFPB diet is not necessarily vegan. Plants are the primary ingredients, but some books and manuals on WFPB eating, also allow a small number of animal ingredients. As a vegan, you can just ignore this and eat 100% plant-based.
Why WFPB?
According to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, “carefully planned vegan diets are healthy, nutritionally adequate and can offer health benefits for the prevention and treatment of certain ailments”2.
Transition to a WFPB diet is not only great for animals and the environment, but it is also beneficial for your own body and health. As supported by various research studies, a WFPB diet not only results in better overall health, but can also result in losing weight and aid the prevention of various diseases. It is clinically proven that a WFPB diet can help prevent and sometimes even reduce chronic illnesses such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes type 2.
How to eat WFPB?
Starting a WFPB diet requires some planning and knowledge of nutrients. So prepare before you start. There are many good online sources and books about a WFPB diet (see book recommendations below). I will give you some basics to start with.
Back to basics
The basics of a WFPB diet are vegetables, grains, and fruits. Make sure your daily meals contain a variety of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats. A healthy balanced meal consists of roughly 75% carbs, 15% protein, and 10% fat.
I can highly recommend that for the first few weeks of transitioning to a WFPB diet, you use an app like cronometer to track what you eat. This allows you to get a better insight into the quantities, ratios, and nutrients of your intake. You do not necessarily have to reach all your daily targets to live a healthier life. Average your intake over one month and see how you are doing. If you are concerned or if you have specific questions, you can always seek the professional advice of a plant-based nutritionist (for a list, scroll down).
Create balanced & varied meals
Vegetables contain few calories. For that reason, it is important to supplement your vegetables with protein-rich sources, which contain more calories.
Sources of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates (carbs) are a vital source of energy and important for a healthy body. Plants contain a great number of carbs and fibers. Your body will quickly absorb the carbs from fruits in your blood. This will give a quick release of energy to the body. Your body takes a lot longer to break down starches, which results in energy release over a longer period of time and a full and content feeling.3
Good sources of complex carbohydrates are whole grain cereals, potatoes, beans, legumes, and lentils. Good sources of simple carbohydrates are fruit and brightly colored vegetables.
Sources of protein
Protein makes you feel full and is essential for the maintenance and build-up of your muscles. When your intake of calories on a WFPB diet is sufficient, your intake of protein will normally be enough. On average your body requires 0,8 grams of protein per kg of body weight. For most people, this results in approximately 50 grams per day. You can use this handy online protein calculator. You do not need to concern yourself with things like "incomplete proteins" or combining proteins.4
Good sources of protein are tofu, tempeh, edamame (soybeans), lentils, chickpeas, peanut butter, almonds, quinoa, chia seeds, beans, potatoes, broccoli, kale & mushrooms.
To ingest a healthy mix of proteins it is recommended that you consume various sorts of legumes on a weekly basis. For instance: chickpeas, lentils, kidney beans, white, brown, black beans, and soybeans. These legumes contain high amounts of protein, iron, vitamin B, and other essential nutrients. If you use canned vegetables, make sure they do not contain too much added sodium and rinse them to get rid of any additives.
Sources of healthy fats
Eating a WFPB diet means you add as little fat as possible. This does not mean, however, that you don’t consume any fat at all. Vegetables, beans, and grains all contain natural fats, but not nearly as much as processed foods or animal products. Approximately 10% of calories in a plant-based diet without added fats are derived from fats.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fats are called essential fats because our body requires them, but cannot produce them. This means we need to get these fats from the foods we consume. These plant-based fats perform many important roles, for instance, the formation of cell membranes and synthesization of hormones.5
It is best to only add healthy fats to your meal in limited quantities and in unprocessed form. Do not use refined oils like olive oil and coconut oil. Oils contain high amounts of calories and barely any nutrients. It is better to eat them as a whole.
Good sources of healthy fats are linseed, chia seeds, avocado, nuts (butters), seeds, and olives.
Fiber
Your body does not have the capacity to digest or absorb fiber, but it is essential for optimal bowel movement and transport in the intestines. For that reason, it is important to consume a sufficient amount of fiber. Fiber can only be found in plants. Vegetables, wholegrain cereals, beans, and fruits are all full of fiber.
Water/Fluids
Water/Fluids are essential for a healthy and properly functioning body. They are not just a requirement for proper digestion and the functioning of other bodily processes, but also make you feel full. When on a WFPB diet, you will get a large portion of your fluid intake from the foods you ingest. Depending on your body type, level of activity, and external factors, you should drink an additional 1.5 liter of water per day. You can also drink (herbal) tea. Refrain from drinking (too much) fruit juice: these contain high amounts of sugar.
WFPB Essentials
To create healthy WFPB meals, the following foods are an essential part of your shopping list:
Vegetables: kale, spinach, tomatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, asparagus, bell peppers;
Starchy Vegetables: potatoes, sweet potatoes, pumpkin/squash;
Whole grains: brown rice, oats, farro, quinoa, brown rice/pasta, barley;
Fruits: berries, citric fruits, pears, peaches, pineapple, bananas;
Healthy fats: avocados, walnuts, olives, unsweetened coconut;
Legumes: peas, chickpeas, lentils, peanuts, black beans;
Seeds, nuts, and nut butters: almonds, cashew nuts, macadamia nuts, pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, natural peanut butter, tahini;
Unsweetened plant-based milks: soy milk, oat milk;
Herbs & spices: garlic, paprika powder, basil, rosemary, turmeric, curry, black pepper;
Sauces and seasoning: salsa, mustard, nutritional yeast flakes, soy sauce, vinegar, lemon juice;
Plant-based protein: tofu, tempeh, plant-based protein sources or powders without added sugars or artificial ingredients;
Beverages: Water, (green) tea, coffee (limited).
Easy WFPB meals
- Ways to create easy Whole Food Plant Based meals
Notes
- Novick, J. https://www.jeffnovick.com/post/the-healthy-eating-placemat-a-visual-guide-to-healthy-eating
- Melina, V., et.al. - J Acad Nutr Diet 2016 Dec;116(12):1970-1980. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Vegetarian Diets.
- Dr. John McDougall - The Starch Solution
- Forks Over Knives - The No-B.S. Guide to Vegan Protein.
- Dr. John McDougall - The Starch Solution
Resources
Books
For more information on a WFPB diet, health, and disease control I highly recommend the following books:
- How not to die? - Dr. M. Greger
- The China Study - Colin T. Campbell & Thomas Campbell
- The China Study Solution. The Simple Way to Lose Weight and Reverse Illness, Using Whole-Food, Plant-Based Diet - Thomas Campbell
- Proteinaholic - Dr. Garth Davis
- Prevent and Reverse Heart Disease. Dr. C. Esselstyn Jr.
- The Starch Solution - Dr. McDougall